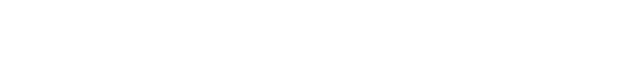Examples of grinding processes by machining center and types of mounted wheels
In the past, jig grinders have been used for precision grinding processes using mounted wheels. In recent years, however, as component shapes have become more complex, there is an increasing need for machining centers (griding centers) with griding specifications that enable more complex processing.
In this article we introduce the problems of grinding in semiconductor manufacturing equipment and the mounted wheels used in machining centers.
- Grinding challenges in semiconductor manufacturing equipment
- What is a machining center (grinding center) with grinding specifications?
- What kind of grinding wheels are mounted in a machining center?
- Mounted wheels / Types of grinding mounted wheels
- Example of grinding processes by machining centers
- Summary of grinding processes by machining centers
Challenges of grinding processes for semiconductor manufacturing equipment

In recent years, the processing of parts for semiconductor manufacturing equipment has increased due to the growing global demand for semiconductors, including those for EVs and 5G (next generation communication systems). In particular, there is a growing demand for processing “quartz glass” and “functional ceramics,” that are chemically stable, in terms of heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance.
Many semiconductor manufacturing equipment parts which require high machining accuracy, are finished by grinding. However, with the increasing complexity of part shapes and the increasing number of difficult-to-machine materials such as highly functional materials, there are also an increasing number of cases where conventional grinders are insufficient for processing. In many instances, finishing becomes possible after passing through multiple machine tools.
Among other things, quartz glass and ceramics, which are often used as materials for equipment parts in the front-end process, require many machining processes, such as pocket machining to place silicon wafers and boring. The challenge is how to improve processing efficiency.
About the semiconductor manufacturing equipment market:
Driven by a succession of huge capital expenditures by the world's major semiconductor manufacturers, the semiconductor manufacturing equipment market was brisk from 2021 to 2022, with the overall global market size reaching a record high for the second consecutive year. ... (Omitted)... The market is expected to expand over the medium to long term from 2024 onward.References: JETRO
What is a Machining Center with Grinding Specifications (Grinding center)

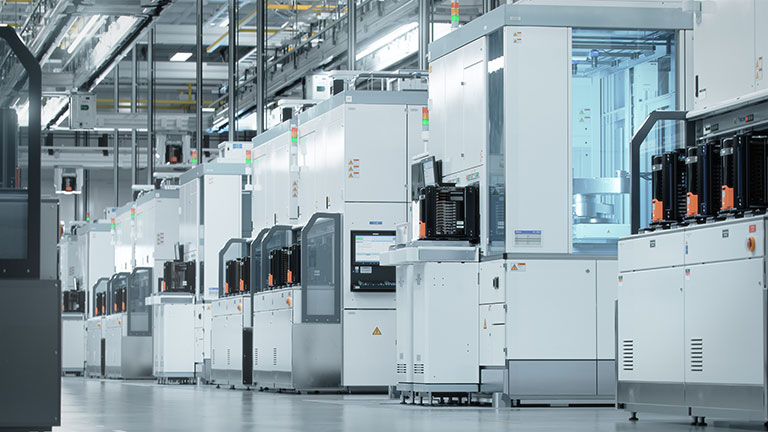
A machining center with grinding specifications is effective in improving the machining efficiency of grinding. The grinding center can be equipped with a "wheel with shafts" for grinding on the ATC, allowing multiple grinding processes to be performed on a single machine.
Especially for 5-axis machining centers, multiple processes such as shape machining, planar machining, and cylindrical machining can be executed with a single chuck, offering the potential for improved accuracy. Efficient machining using machining centers is becoming increasingly popular for some processes, such as surface grinders and cylindrical grinders.
◎About grinding specifications
Griding centers are equipped with a special sealing and other dustproof measures to protect each shaft, including the sliding parts and guides, from the sludge (powdered chips) specific to grinding. Caution should be exercised when grinding on a standard machining center to avoid machine damage and extend its service life.
What kind of grinding wheels are mounted in a machining center?

The "wheel with shafts" is an indispensable tool for grinding on a machining center. Very similar to cutting tools, mounted wheels are held by shanks and mounted on the ATC.
Grinding that can be done with a wheel with a shaft is not limited to finishing. Even with hard and brittle materials such as quartz glass and ceramics, it is possible to “drill” and “groove” with the same precision as drills and milling machines.
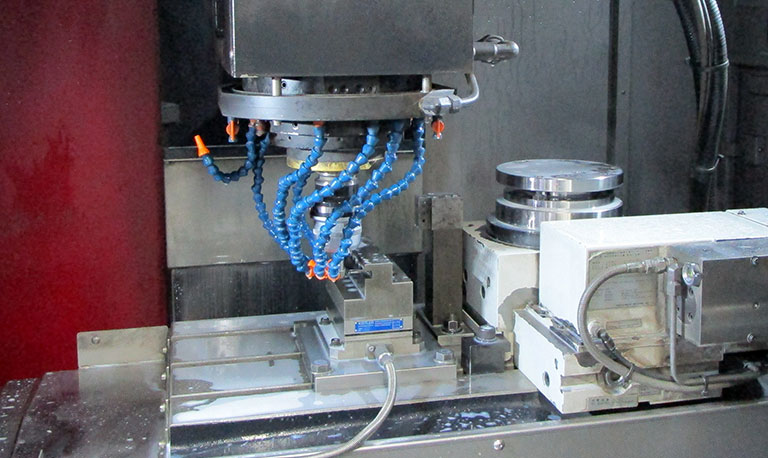
In addition, since all of the abrasive grain layers are used as cutting edges, it is also possible to finish the "bottom surface" and "outer peripheral surface" simultaneously, just like an end mill.
◎Point of Machining
- Due to having a higher number of cutting edges compared to typical milling tools, for machining that utilizes the bottom surface, it is advisable to use a coreless tool with a smaller contact area.
What can be done with mounted wheels?
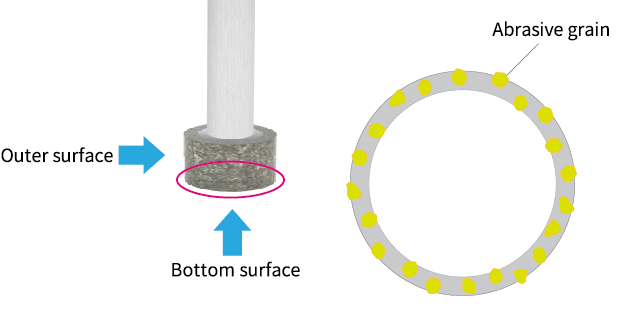
Front-side machining with grinding wheels
Front grinding can be performed by using a "coreless tool" or "cup shaped wheel".
Cup-type mounted wheels of around φ30 to φ50 can also be manufactured, enabling efficient grinding of large surfaces.
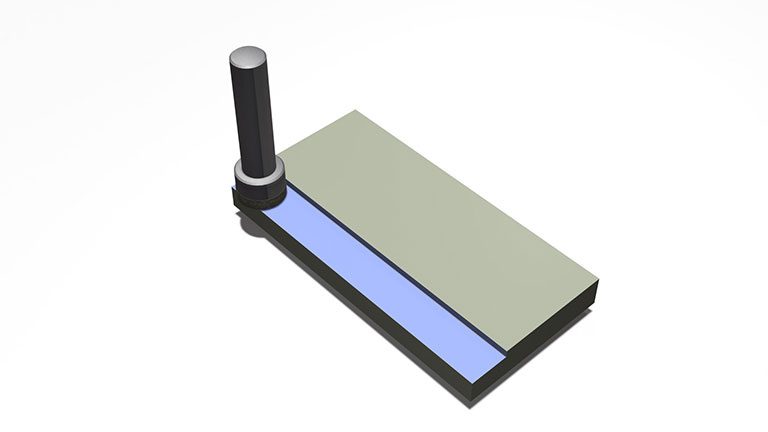
Pocketing/cavity machining with grinding wheels
Pocketing/cavity machining is possible by using "center-through tool" or "coreless tool".
For small pocket machining, the use of a center through tool with an eccentric channel allows machining with no residual core, even when the tool swing is small. The absence of a core allows for better coolant flow and can contribute to increased efficiency.
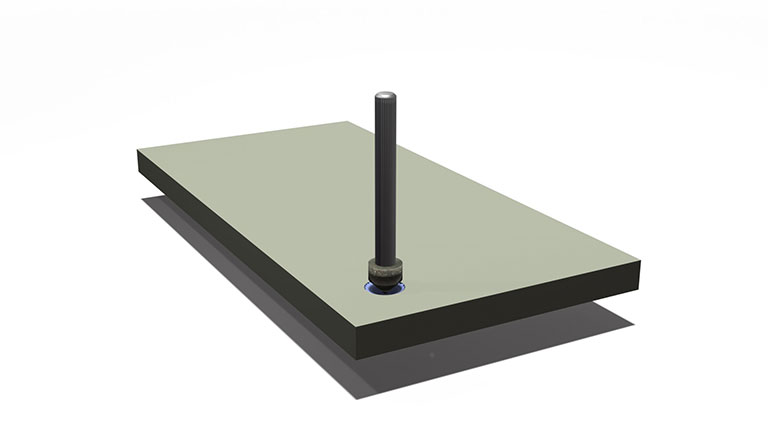
Hole chamfering with grinding wheel
Chamfering can be performed by using "wheels with metal and electroplated shafts" with a tapered angle at the tip.
By using inverted R-shaped wheels with electroplated shafts it is possible to perform R chamfering.
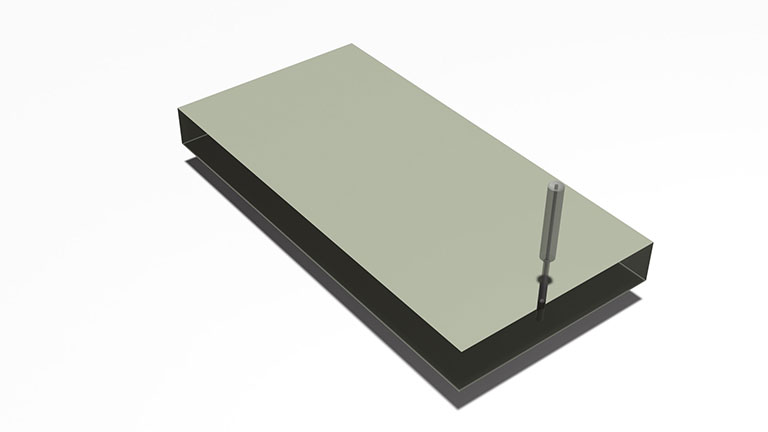
Drilling with grinding wheels
Bore machining using grinding typically involves helical machining. However, employing a "center through drill" with a metal bond allows for drilling straight down holes with vertical feed exclusively.
Compared with helical machining, this method reduces drilling time and is more efficient.
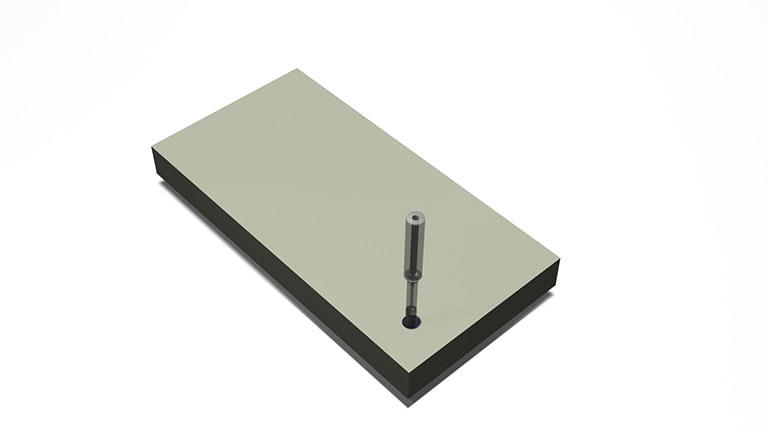
Bore machining with grinding wheels
The machining of holes through helical techniques can be accomplished using metal bond tools such as the "center through tool," "coreless tool," or "wheel with a small-diameter electrodeposition shaft."
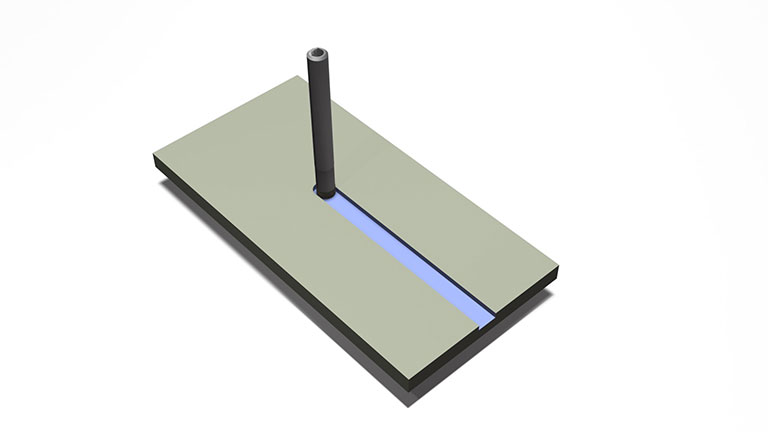
Grooving with grinding wheels
Utilizing metal bond tools such as the "center through tool," "coreless tool," and "wheel with a small-diameter electrodeposited shaft," grooving through helical machining and trochoidal machining becomes feasible.
(Note: when employing a one-directional tool path like ramping, there is a tendency for chips to accumulate at the machining point. Hence, it is advisable to design a tool path that facilitates efficient chip removal.
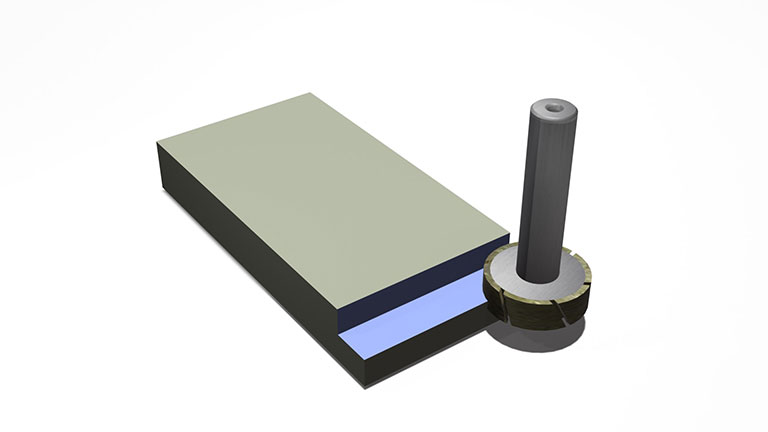
Shoulder milling with grinding wheels (front face + periphery)
Efficient shoulder milling can be done by using a "general purpose contouring tool" with a slit.
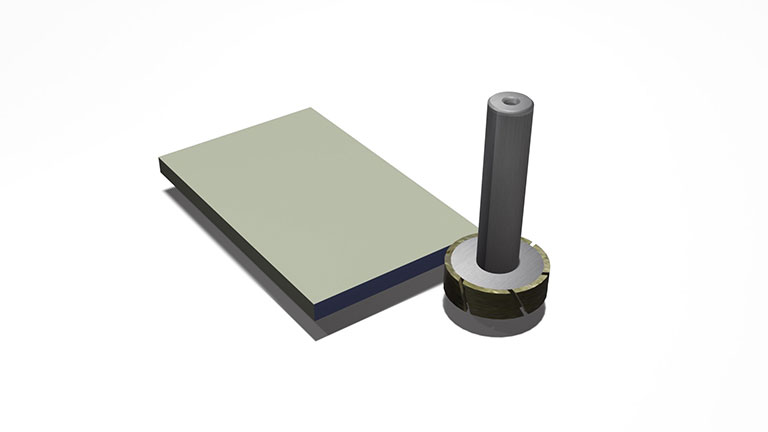
Outer contouring with grinding wheels
Outer contouring can be performed by using a "wheel with metal bond shafts" with a diagonal slit.
Straight mounted wheels can also be manufactured, and with a 5-axis machine, cylindrical grinding can be performed by rotating the workpiece on the C-axis.
Types of mounted grinding wheels and mounted wheels
Tokyo Diamond Tool Works offers a wide lineup of "mounted wheels" for machining centers that can handle complex shapes and a variety of hard and brittle materials.
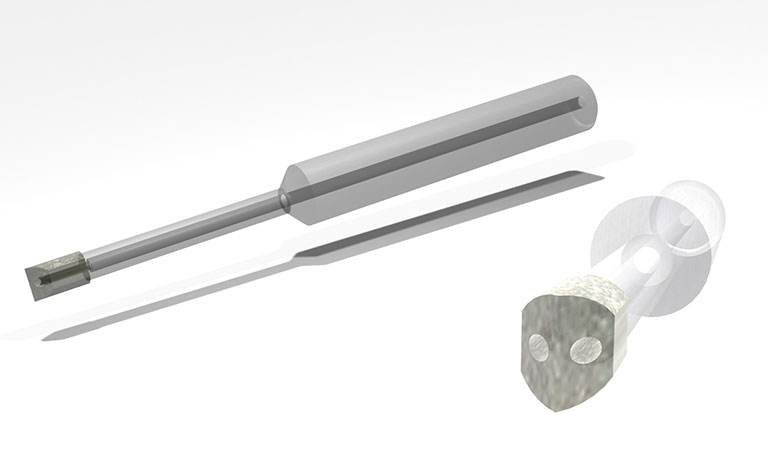
Mounted wheel for helical machining (center-through)
This is a metal bonded small-diameter tool with an eccentric hole (center through structure) that can be used universally.
Due to the lack of chip discharge, drilling by plunging is not feasible. Avoid utilizing this tool for contouring with the peripheral side.
(Note: For flat surfaces machining applications, use coreless tools with diameter of φ4 or larger.)
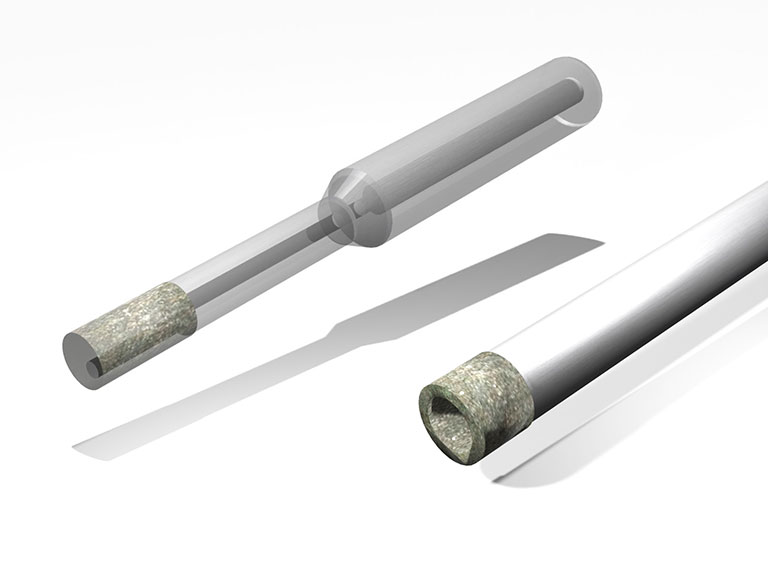
Mounted wheel for drilling (center-through)
This metal-bonded center-through wheel is designed for drilling, without the need for helical machining, utilizing only axial feed.
(Note: It is not recommended for reaming to achieve a final bore diameter with consistent accuracy due to potential tool wear.)
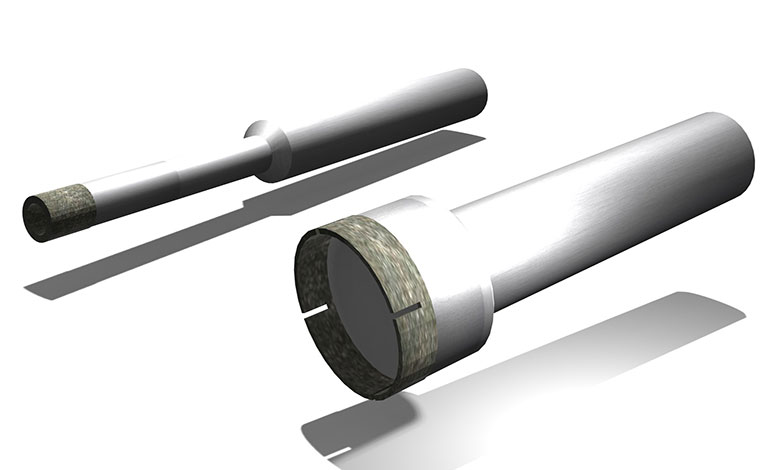
Mounted wheel for helical machining (coreless)
This is a general-purpose metal bond tool with a coreless structure that eliminates the zero peripheral speed point.
The center-through design is also available, but the shaft rigidity is lower for smaller diameters. Also, φ8 or larger designs with slits are available.
(Note: For core removal ‘trepanning’ processing, please use core tools or core bits. Core tool and core bit should be used for core punching and trepanning.)
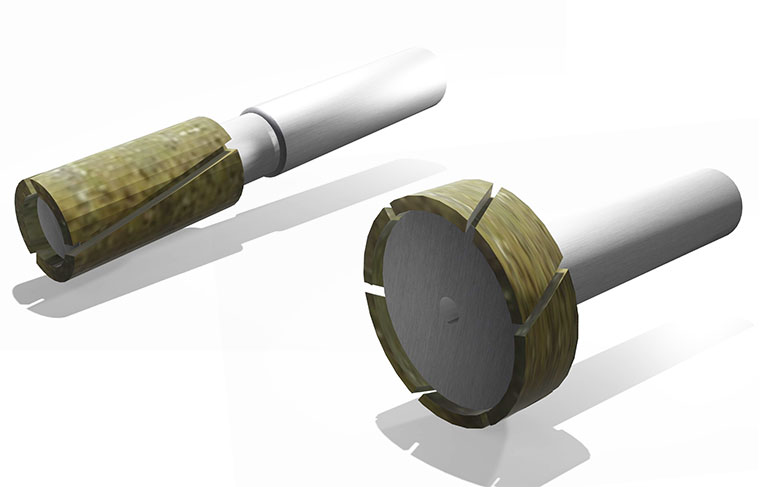
Mounted wheel for Contouring
This metal bond contouring tool is primarily employed on the tool periphery side, featuring a standard slanted slit design. The slit inclination is tailored for spindle clockwise (right) rotation, while a center-through design is also an option.
Due to the slit reaching up to the tip surface, it proves efficient for shoulder milling applications.
Example of grinding process by machining center
The following is an example of machining a sample workpiece (a complex shape resembling Colosseum) using a machining center and wheels with a shaft.
In the machining examples, hard and brittle quartz glass is machined with one chuck, from rough machining to finishing.
◎Points of machining
- Hard and brittle materials are prone to chipping, particularly on the exit side. So, extra caution is required.
- In the sample workpiece, we achieved precision grinding and finishing of hard and brittle quartz glass by carefully designing the grinding tool paths.
Summary of example of grinding process by machining center
Tokyo Diamond Tool Works provides optimal mounted wheels tailored to the workpiece type and shape. These are used for grinding various materials like quartz glass for semiconductor manufacturing equipment, SiC ceramic, AIN aluminum nitride, silicon nitride, alumina ceramics, silicon, and more. Additionally, we offer in-house evaluations utilizing our machining centers (grinding centers).
If you have any questions about the selection of tools for working with brittle materials on machining centers or grinding centers, please contact us for more information.